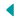
Global Warming: A Zonal Energy Balance Model
This teaching module, developed by Victor Padron of Normandale Community College, is directed to undergraduate students in applied mathematics. It introduces a Zonal Energy Balance Model to describe the evolution of the latitudinal distribution of Earth’s surface temperature subject to incremental levels of cumulative carbon emissions in the atmosphere. A strategy to avert “dangerous levels” of global warming is imbedded in the model. Students working with the module will write a MATLAB script to solve the model numerically and apply it with their own choice of the relevant parameters to obtain the solution that guarantees controlled levels of global warming.

Photo credit: Gerard Van der Leun (CC BY-NC-ND 2.0)
Tracking Groundwater Pollution
This teaching module, also developed by Victor, presents an introduction to modeling ground water pollution, directed to undergraduate students in applied mathematics. It begins with a brief discussion of Darcy’s law concerning the flow of a fluid through a porous medium. A mathematical model that uses field data to track ground-water contamination is presented. Students working with the module will write a MATLAB script to obtain a numerical solution of the model and apply it to investigate a real event of groundwater pollution.

Photo credit: Chesapeake Bay Program (CC BY-NC 2.0)